After the Saudi Council of Ministers approved the National Cyber security Strategy, many governmental, private and non-profit organizations seek to adhere to security recommendations and controls that help protect the information assets of the Kingdom and ensure access to a safe and reliable Saudi cyberspace that enables growth and prosperity.
The process of implementing cyber security is a long journey that needs to activate a set of practices at the level of individuals, processes and technical security systems. In this context, Renad Almajed Group (RMG) provides many consulting services that help draw a roadmap for this journey by following security technologies. In ISO 27032 (ISO / IEC 27032: 2012) consistent with the regulations and guidelines issued by the National Cyber security Authority.
ISO 27032 What is it and how did it originate?
The ISO 27032 specification provides a set of guidelines for improving the cyber security situation in the organization through the development of a security framework based on risk management and will cover in particular:
- Information Security
- Network security
- Internet safety
- Protection of information infrastructures

The specification appeared for the first time in the seventh month of 2012 after a significant increase in the number of cyber crimes worldwide during the period between 2000 to 2012. For example, in 2010, the spread of the Zeus Trojan Horse led to the theft of more than 70 million people. Dollars from American banks. These attacks also targeted many other sectors, such as government institutions, health facilities, transportation companies, and many major factories.
In 2011, a group of hackers stole the information of 77 million Sony Corporation customers.
According to Forbes, global spending on cyber security is expected to reach 123 billion US dollars in 2020, as government institutions, private companies and non-profit organizations spend on cyber security continues to grow, defying the economic downturn caused by the Corona virus.
Cyber security and cyberspace
Cyberspace can be defined as the virtual place in which everyone around the world practices their daily activities such as studying, working, shopping, communicating and searching for other services. According to specification 27032, cyberspace can be described as a complex environment resulting from the interaction of people, programs and services on the Internet through technical devices. Modern, connected to global networks, which do not exist in any physical form, but only hypothetically.
As for cyber security, it is all matters related to cyber security through the security measures that protect it.
The task of ISO 27032 (ISO / IEC 270032: 2012) is summarized in providing a set of guides and recommendations to ensure the interaction of security with the virtual environment of cyberspace.
The controls provided by the ISO 27032 Cyber security Management System (ISO / IEC 27032: 2012) are technical controls that are characterized by identifying technical aspects of cyber security (application of level controls, server protection, end user protection, social engineering attack controls, etc.).
Benefits of obtaining a cyber security management system (ISO / IEC 27032: 2012)
There are many benefits resulting from implementing a cyber security management system, for example:
- Protecting organization data and privacy from cyber threats.
- Strengthening regulation in creating and maintaining a cyber security program.
- Improve the security system of the institution and the continuity of its business.
- Detect and monitor attacks.
- Faster response and recovery in the event of an accident.
- Fewer incidents and IT vulnerabilities.
- Increase the credibility and confidence of customers and suppliers.
- Increased confidence of stakeholders in the security measures followed by the cyber security department.
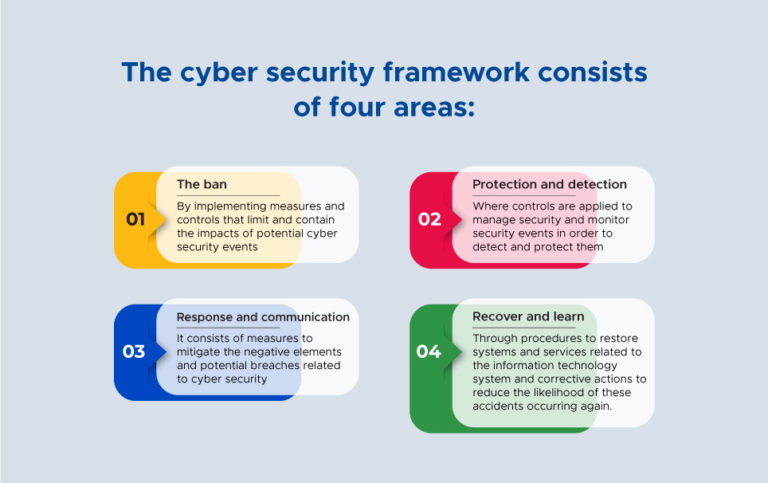
Cyber security Management System Framework (ISO / IEC 27032: 2012)
The ISO 27032 specification provides a framework for addressing the establishment of trust, cooperation, exchange of information and technical guidance, ensuring the formation of an integrated system that brings together stakeholders in cyberspace.
The cyber security framework consists of four areas:
- The ban
By implementing measures and controls that limit and contain the impacts of potential cyber security events
- Protection and detection
Where controls are applied to manage security and monitor security events in order to detect and protect them
- Response and communication
It consists of measures to mitigate the negative elements and potential breaches related to cyber security
- Recover and learn
Through procedures to restore systems and services related to the information technology system and corrective actions to reduce the likelihood of these accidents occurring again.
Methodology for building a cyber security management system (ISO / IEC 270032: 2012)
The cyber security system is built through four phases:
Stage one: understanding the organization
Understand the products and services provided to internal and external clients, security regulatory framework and collection
Security documents with technical security measures in place, provided that this process is done by reviewing:
- Operations and functions include
- Departmental organizational charts
- The relationship of sites, operations, and dependencies
- Cyber security job descriptions
- Main actions
- Data centers and computer and communication rooms
- Including physical, environmental and others
- Computer facilities.
- Hardware (servers and storage systems)
- Communication systems
- Grids and Charts
- Storage location for discs, tapes, etc.
- Physical security including access control
- Cables, heating, air conditioning and fire protection devices
- Other computer related equipment
- High availability, clustering, disaster recovery solutions, and more for every server, system, storage device, and other equipment.
- Virtualization and load balancing
- Networking (LAN, WAN, etc.) and setting up connections
- Information security policies, strategies and procedures.
- Software
- Operating systems and systems software
- Databases
- Applications
- Other programs and systems
- Archiving storage policies and procedures
- Data files
- Software
- Spin frequency
- Other existing controls and policies such as ISO 27001 (IS0 / IEC27001: 2013).
- Current local legislation and regulatory requirements.
- Current document management procedures, corrective action procedures, preventive measures, operational risk procedures and internal audit procedures (if any).
The second stage: risk analysis
The risk assessment will identify the surrounding and environmental events (internal and external) that could adversely affect the organization and its facilities by disruption as well as disasters, the damages that these events could cause, and the controls needed to prevent or reduce the effects of potential loss.
Here are some types of threats that you can consider.
- Natural (such as earthquakes, floods, fires, etc.)
- Technology (such as power loss, communication failure, ICT infrastructure failure, viruses, information system security, hardware failure, etc.)
- Man-made (such as sabotage, major accidents / events, human errors, terrorism, operational errors, fraud, bad project management, etc.)
- Social Risk assessment will be applied to departmental processes, focusing on processes, activities and resources (systems, work area, technology, etc.)
The purpose of the risk assessment study in cyber security management will be:
Identify internal and external threats, vulnerabilities, responsibilities, and exposure that could cause disruption, temporary or permanent disruption, or loss of high-priority operations, activities, resources, systems, and applications for the organization, including but not limited to:
- Internal resilience and infrastructure reliability (such as network vulnerabilities, sites, and personnel)
- External threats such as partner failure, weather conditions, natural disasters, accidents, and sabotage
- Threats from other interconnected networks
- Identify concentrations of hazards and points of failure (including individual points of failure) and weaknesses in all resources required to continue operating for each critical activity
- Determine the likelihood (likelihood or frequency) of a threat, exposure and vulnerability to identified threats and assess their impact on network operation and services provided, taking into account identified weaknesses and vulnerabilities
- Provide a basis for the organization’s risk mitigation program and management control program and action plan.
Project risk assessment approach
Once the key processes and activities important to the mission, services, resources, etc. are identified, and their business values are defined, our risk assessment approach will include the following steps:
- Step 1 – Identify and Identify Threats
- Step 2 – Identify and characterize existing protection and mitigation measures
- Step 3 – Identify and distinguish weaknesses
- Step 4 – Estimate the possibilities and consequences
- Step 5 – Assess and evaluate risks
Risk assessment considerations may include:
- Recurrence of certain types of disasters (often or rarely)
- Rapid appearance (suddenly or gradually)
- The levels of redundancy present and required throughout the organization to accommodate critical systems and functions, incorporate typical options for risk mitigation
- Avoid risks
- Accept the risks
- Control of risks
The third stage: the cyber security plan
At this stage, and thanks to the work that was carried out in the previous stages, a plan will be developed that allows knowledge of the priorities and measures that must be developed to achieve cyber security requirements.
This plan will face different strategies that have to be applied at different levels of the organization, including:
- Cyber security policies
- Define roles and responsibilities
- Technical controls
The main areas to be considered include
- Resource options
- Related high-level systems, technologies and infrastructure
- Major suppliers and third parties
Provide recommendations for improvements to the infrastructure, systems, applications, technologies, interfaces, architecture, network, and resources of cyber security management:
- Improved application and system availability (for example, automatic failover where evidence is located)
- Site infrastructure optimization (such as UPS, cooling, security, etc.).
The fourth stage: implementation
The stage that usually requires the greatest effort, as all the procedures specified in the previous stages will be reflected and aims to oblige everyone who implements them to be proactive in security measures, with a great focus on prevention mechanisms in operations that use cyberspace. This stage will then focus on implementing Controls that must take into account the level of maturity in current security management, application of security policies, implementation of correct frameworks for information exchange, ensuring the implementation of employee awareness plans, application of electronic phishing systems, monitoring of information and communication technology, with additional controls including application control, data validation, protection from attacks and operations Server level controls, patch management, monitoring, periodic reviews and security checks. Operating system updates, antivirus, tools, and security settings.
How to start implementing a cyber security management system (ISO / IEC 27032: 2012)
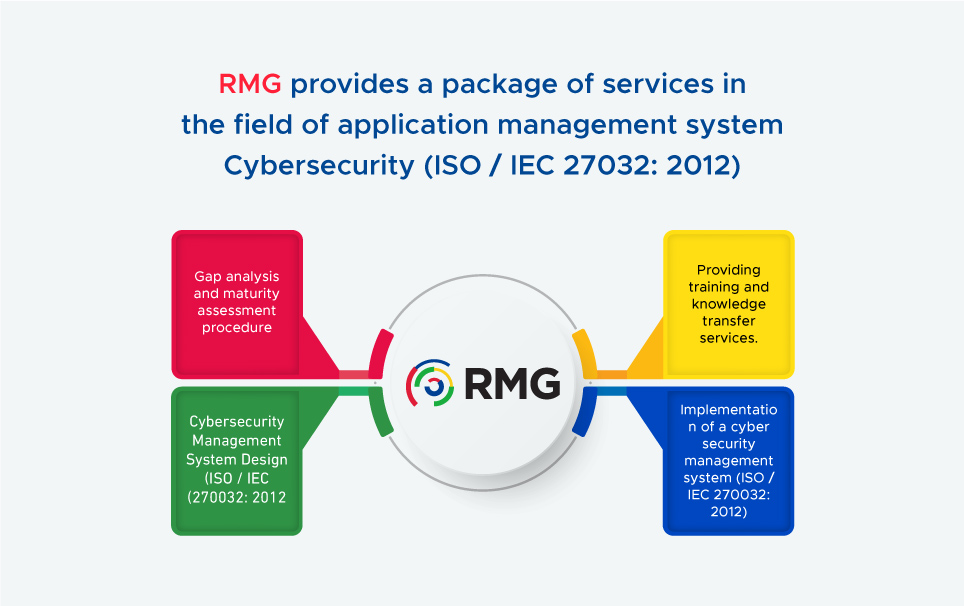
Any successful application process starts from analyzing the gap accurately and Renad Almajed Group (RMG) is one of the first Saudi companies to successfully implement a cyber security management system (ISO / IEC 270032: 2012). The company provides a package of services that can be summarized as:
- Gap analysis and maturity assessment procedure.
- Cybersecurity Management System Design (ISO / IEC 270032: 2012)
- Implementation of a cyber security management system (ISO / IEC 270032: 2012)
- Providing training and knowledge transfer services.