Blog Body
Discover the secrets of successful project planning with our comprehensive guide. Learn how to develop an integrated project plan, identify resources, manage risks, and efficiently achieve your goals with Renad Al Majd experts to turn your vision into reality.
Projects are the primary engine for growth and innovation. But what separates a project that achieves brilliant success from one that falters before seeing the light of day? The answer lies in one word: planning. Project planning is not just a routine administrative step; it’s the art and science of drawing a roadmap that ensures a project reaches its desired destination safely and efficiently.
Neglecting this vital stage is like sailing on a turbulent ocean without a compass or map, where the results are ambiguous and the risks are high. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the concept of project planning, explore its stages, benefits, and key elements, to provide you with the knowledge needed to transform your ambitious ideas into successful and sustainable projects.
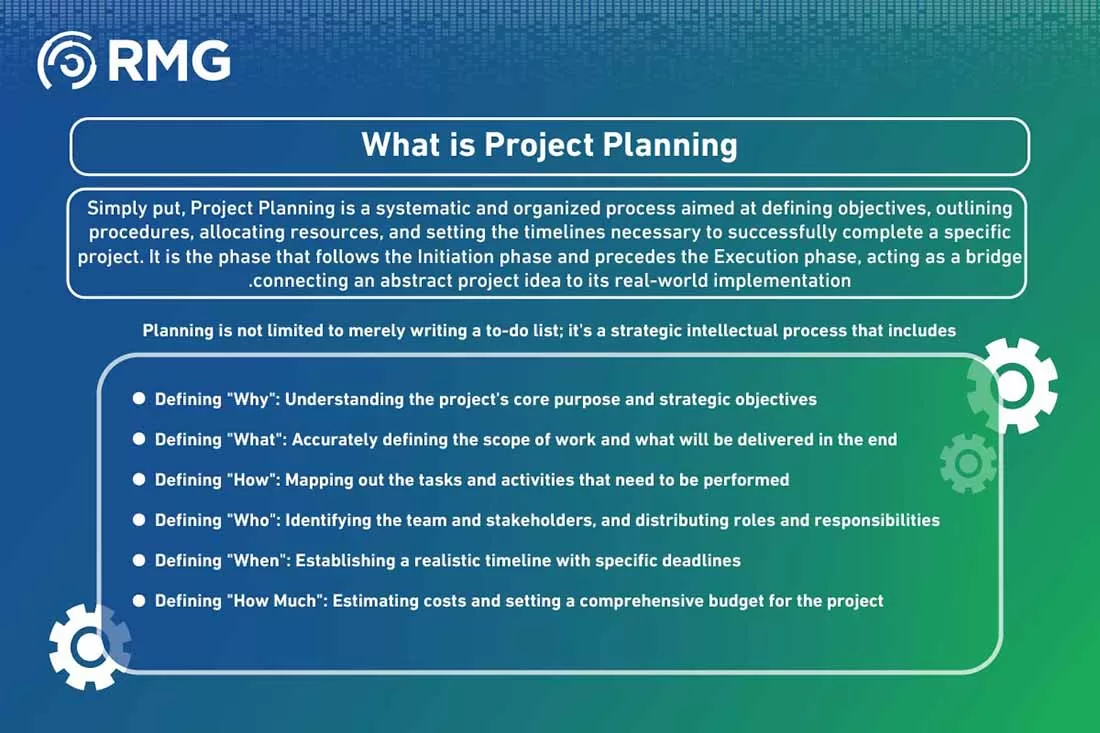
What is Project Planning?
Simply put, Project Planning is a systematic and organized process aimed at defining objectives, outlining procedures, allocating resources, and setting the timelines necessary to successfully complete a specific project. It is the phase that follows the Initiation phase and precedes the Execution phase, acting as a bridge connecting an abstract project idea to its real-world implementation.
Planning is not limited to merely writing a to-do list; it’s a strategic intellectual process that includes:
- Defining “Why”: Understanding the project’s core purpose and strategic objectives.
- Defining “What”: Accurately defining the scope of work and what will be delivered in the end.
- Defining “How”: Mapping out the tasks and activities that need to be performed.
- Defining “Who”: Identifying the team and stakeholders, and distributing roles and responsibilities.
- Defining “When”: Establishing a realistic timeline with specific deadlines.
- Defining “How Much”: Estimating costs and setting a comprehensive budget for the project.
Effective planning acts as the project’s mastermind, providing clarity and direction and helping anticipate challenges before they arise.
What is a Project Plan?
If “project planning” is the process, then a “Project Plan” is the final product and the tangible output of that process. A project plan is a formal, detailed document that serves as a primary reference and guide for all project participants, from the project team to senior management and stakeholders.
This document is not just a static record; it’s a dynamic tool that is constantly updated and reviewed to reflect work progress and any changes that may occur. A typical project plan contains a set of sub-plans covering all aspects of the project.
What are the Essential Project Planning Phases?
The project planning process consists of several interconnected phases that ensure comprehensive coverage of all success requirements. These phases can be summarized as follows:
- Defining Goals and Scope: The journey begins with a clear definition of what success looks like. In this phase, project goals (preferably SMART: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound) are defined, and the scope of work is accurately documented, specifying what is included and excluded from the project.
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): Large project deliverables are broken down into smaller, more manageable tasks. This is known as the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS), which helps in more accurate time and cost estimation.
- Developing the Schedule: After defining tasks, the duration of each task is estimated, dependencies between them are identified (i.e., tasks that depend on the completion of other tasks), and then a comprehensive project schedule is developed, with key Milestones identified.
- Resource and Budget Planning: All necessary resources (human, financial, material, technical) are identified and allocated to different tasks. Based on this, a detailed budget covering all estimated project costs is prepared.
- Risk Management Planning: No project is without risks. In this phase, potential risks (internal and external) are identified, their probability and impact are assessed, and proactive plans are developed to deal with or mitigate their effects.
- Communication Plan Development: Effective communication is the lifeline of any project. Key stakeholders are identified, the information they need is determined, the frequency of communication, and the channels to be used (meetings, reports, email) are established.
What are the Benefits of Successful Project Planning?
Investing time and effort in good planning yields numerous benefits for the project and the organization as a whole, most notably:
- Clarity of Vision and Purpose: Ensures that all team members and stakeholders are fully aware of the project’s goals and requirements.
- Improved Resource Management: Allows for optimal allocation of available resources, preventing waste and increasing efficiency.
- Budget and Time Control: Provides a solid foundation for monitoring costs and adhering to the schedule, and helps in taking early corrective actions.
- Risk Reduction: Proactive risk planning helps avoid many potential problems and minimizes the impact of unavoidable issues.
- Enhanced Communication and Collaboration: The project plan provides a common language and a central platform for information, improving coordination among team members.
- Increased Chances of Success: Projects that begin with a strong plan are more likely to achieve their goals on time and within budget.
Essential Elements in Project Planning
A comprehensive project plan consists of several integrated components or sub-plans, including:
- Scope Management Plan: Explains how the scope will be defined, verified, and controlled.
- Schedule Management Plan: Determines how the schedule will be developed, monitored, and updated.
- Cost Management Plan: Specifies how the budget will be estimated, funded, managed, and controlled.
- Quality Management Plan: Defines project and deliverable quality standards and how to ensure they are met.
- Resource Management Plan: Explains how necessary resources will be identified, acquired, and managed.
- Communications Management Plan: Determines stakeholder information needs and how to meet them.
- Risk Management Plan: Documents how risks will be identified, analyzed, and responded to.
- Procurement Management Plan: Identifies goods and services to be purchased from outside the organization.
- Stakeholder Engagement Plan: Defines strategies for effectively engaging stakeholders throughout the project lifecycle.
The Concept of Project-Based ERP
In the context of large and complex projects, the term Project-Based ERP emerges. This is an extension of the traditional Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) concept, but specifically designed to meet the needs of organizations whose core business revolves around projects.
A Project-Based ERP system integrates all aspects of a project (planning, budgeting, resources, execution, invoicing) with other enterprise functions such as finance, human resources, and supply chain. This integration provides a comprehensive and real-time view of project performance and financial health, allowing for more accurate and strategic decision-making.
How to Plan Small Projects Effectively
Not all projects require the same level of bureaucratic detail. For small projects, the planning process can be simplified while maintaining effectiveness by following these tips:
- Focus on the Essentials: Start with a simple document outlining the goals, key deliverables, timeline, budget, and roles and responsibilities.
- Use Simple Tools: There’s no need for complex software. Tools like Trello, Asana, or even Excel spreadsheets can be sufficient for tracking tasks and progress.
- Direct Communication: In small teams, direct and frequent communication is often more effective than formal communication plans.
- Be Flexible: Small projects often require greater flexibility. Be prepared to adapt the plan as circumstances change.
Key Benefits of Using Project Planning Tools
Whether your project is large or small, using dedicated project planning tools and software offers numerous advantages, including:
- Centralized Information: Gathers all project-related information in one place, making it easy to access.
- Improved Collaboration: Allows team members to collaborate in real-time and easily share updates and files.
- Visibility and Transparency: Provides dashboards and visual reports that clearly show project progress to all parties.
- Task Automation: Automates repetitive tasks such as sending reminders and generating reports, saving time and effort.
Renad Al Majd: Your Strategic Partner in Project Planning and Execution
Understanding the principles of project planning in theory is one thing; applying them effectively in practice is entirely another. This is where expertise and professionalism come into play. At Renad Al Majd (RMG), we understand that meticulous planning is the cornerstone of every successful project. We don’t offer off-the-shelf solutions; instead, we act as your strategic partner, delving into the details of your vision to design customized plans that ensure your goals are achieved.
Renad Al Majd offers a comprehensive suite of services that support your project journey from idea to success:
- Comprehensive Feasibility Studies: Before starting planning, we help you assess the feasibility of the idea from all aspects (financial, technical, marketing) to make an informed decision.
- Project Management Consulting: Our certified experts provide support and guidance throughout all project phases, from developing the project charter to successful closure.
- Integrated Project Plan Preparation: We develop detailed action plans, including scope definition, timelines, budgets, and risk and quality management plans, in line with international best practices.
- Establishing and Managing Project Management Offices (PMO): We help organizations build their internal capabilities by establishing Project Management Offices that standardize practices and enhance project execution efficiency across the enterprise.
- Resource Planning and Management: We ensure optimal utilization of your resources through precise analysis and effective planning that balances project requirements with organizational capabilities.
The Difference Between Project Management and Project Planning
These two terms are often confused, but it’s important to understand the difference:
- Project Planning: Is a fundamental phase within the project lifecycle. It focuses on preparing for the future and setting the roadmap. It answers the questions “What,” “How,” and “When.”
- Project Management: Is the overarching process that extends across all project phases (Initiation, Planning, Execution, Monitoring and Controlling, Closure). Management uses the “Project Plan” as a key tool to guide and monitor work, deal with changes, and ensure objectives are met.
In short, planning is drawing the map, and management is leading the entire journey using that map.
Practical Steps for Professional Project Planning
To translate theory into reality, follow these practical steps:
- Start with a Project Charter: An initial document outlining the project’s purpose, main objectives, and key stakeholders.
- Set SMART Goals: Make your goals Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
- List Deliverables: Clearly define everything that needs to be delivered at the end of the project.
- Create a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): Break down large deliverables into small, actionable tasks.
- Draw a Gantt Chart: Use it to create a visual timeline showing tasks, their durations, and dependencies.
- Estimate the Budget: Calculate the costs associated with each task and resource.
- Identify Risks: Brainstorm all potential obstacles that could derail the project.
- Develop a Response Plan: For each risk, define the actions you will take if it occurs.
- Consolidate Everything into a Project Plan: Document all the above in a formal project plan.
- Hold a Kick-off Meeting: Gather the team and stakeholders to review the plan and ensure everyone is on the same page before execution begins.
Turn Your Vision into Reality: Start Your Project Success Journey with Renad Al Majd Today
Are you a government entity seeking to achieve the goals of Vision 2030 with pioneering projects? Or a private company aspiring to expand and grow through strategic initiatives?
No matter the size or complexity of your project, success begins with one correct step: professional planning. At Renad Al Majd, we don’t just provide consulting; we are committed to being your partners in success. We transform complexities into clarity, risks into opportunities, and plans into achievements you’ll be proud of.
Don’t leave the success of your projects to chance. Contact us today and let our team of experts help you build a solid foundation for a bright future. With Renad Al Majd, your vision is in safe hands.