Data Management Solutions
Data modeling and structuring solutions and data warehouses
Data Modeling:
A data model is basically a visual representation that describes the connections between different data points and structures stored in an information system. The structure determines how the data is stored and how the system will access it. Effective data modeling software is needed to have a proper data structure. When conducting due diligence on leveraging your data to support business decisions, the integrity of said data is a critical prerequisite.
Before calculating their data for valuable insights, business analysts must have complete confidence in the accuracy of the input and the reliability of their data. Any errors during data entry naturally mean a corrupted output as well as redundancy across the database.
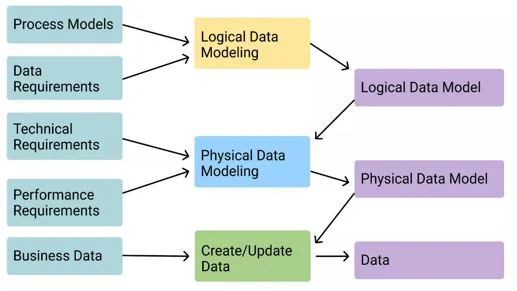
The Three Layers of the Data Model
Are you aiming to migrate to a new system, perhaps upgrade an existing one, or perhaps create a data warehouse that will yield insights? Either way, your data will be organized using the Data Warehouse Modeling tool into one of the following three distinct layers, each with a specific position and function. Let’s dive into each layer individually:
Conceptual Data Model:
This is the basic level of the model that defines the structure of the data according to the requirements of the business. It focuses on attributes, inputs, and business-oriented relationships.
- It provides organization-wide coverage of business concepts.
- It caters to a specific business audience.
- The conceptual layer is built independently of any hardware specifications, storage capacity, or software limitations The focus is on the representation of the data as it is displayed in the real world.
Boolean Data Model:
This layer is more complex and structured than the conceptual layer. It contains information on how to implement the model by defining the structure and relationships of data elements. The main advantage of a logical model is that it provides a stable foundation for a logical and physical data model.
- The logical model lists the requirements of the project, but it can also integrate with other data models depending on the scope.
- Designed and developed independently of
- Data types of data elements have a precise length.
Physical Data Model:
The physical layer shows how to implement the data model in a database management system. It simplifies the implementation methodology in the form of tables, indexes, division, etc. A physical data model diagram helps visualize the entire database structure.
- A physical model lists the needs of a single project, but depending on the scope of the project, it can also integrate with other physical models.
- For accurate data representation, all columns must have an accurate data type, default values, and length.
Technical Architecture and Data Structuring
The importance of this lies in the fact that when choosing a technology, it is necessary to balance the needs of the organization over the extent of its strategy and the expected investments, whether in terms of providing those technologies, the operational costs for them, or the cadres required to work on them, so that Although the beginning is to provide capabilities that serve the purpose in the short term, their limitations in expanding the capabilities and their inability to adapt to the expected development in requirements may lead to the cessation of investment and the difficulty of transitioning to another technology.


When identifying the needs of technologies, we have to classify them into five main components and adapt each of them to the requirements of the business intelligence journey, these components represent the journey of data from its sources in the systems to the unified source, which is the data warehouse until its use through the business intelligence platform or specialized data analysis tools, and for the purpose of summarizing it in a simplified way, and in case of the need to view the details, each of them is searched separately from the many available sources, whether consulting sites or Even through the websites of technical companies, so I preferred to shorten it here in the following form to facilitate the delivery of information:
First: Data Extracts and Ingestion
There are several types of programs and tools specialized in extracting and collecting data, but choosing the appropriate one depends first on determining the types of data in terms of whether it is structured data or unstructured, as well as the quality of databases in the source system may require making sure that the appropriate programs are selected for them, also the requirements must be determined in terms of the periodicity of data extraction, such as if the requirements are to be updated instantaneously, this may require specialized programs in the real-time extraction of data without affecting the The operational processes that take place in those systems.
Second: Data Processing and Storing
There are several types of programs and tools specialized in extracting and collecting data, but choosing the appropriate one depends first on determining the types of data in terms of whether it is structured data or unstructured, as well as the quality of databases in the source system may require making sure that the appropriate programs are selected for them, also the requirements must be determined in terms of the periodicity of data extraction, such as if the requirements are to be updated instantaneously, this may require specialized programs in the real-time extraction of data without affecting the The operational processes that take place in those systems.
Third: Data Management and Monitoring Component
In this part, the standards are applied and the quality of the data is measured according to the procedures that have been done through data governance with the data owners, so that through this stage, the updated data is documented and audited and the data owner and the beneficiaries are notified of any exceptions that have occurred to the standards to take the necessary corrective action and avoid the impact of this on the decision makers, also through this stage, the new data that has been added is explored to take its course in data governance, so it starts by alerting the data administrators to work on Identify the main owner of such data and the necessary procedures to complete the governance of the data.
Fourth: Partial Data Utilization
This last part is what the end user sees in the data journey, after it has been extracted from the systems and stored in a unified source and applied to the standards and procedures for data management before it is ready for use. Tools and programs vary according to the nature of use, starting with operational reporting programs, of which Excel may be the most famous and flexible in spreadsheets, but the need for programs with better capabilities is developing than the application of dashboards or analytical reports, and more so for predictive model programs and advanced analytics, until we reach complex programs required by data scientists and the application of artificial intelligence technologies, which vary according to the purpose and are usually in the form of mini-projects.
Fifth: Data Security and Access Authorization
In this part, the tools used in protecting data and granting access to it must serve all stages in the data journey from the source to the reports, as there are protection and encryption tools that are applied when extracting and pulling data from the source, as well as encrypting it from moving to the data lake and data warehouse so that access to it is blocked except according to permissions, and similarly at the level of reports so that there are groups of access rights to the reports. These tools must comply with the application of data governance when classifying The extent of the confidentiality or sensitivity of that data, where the owner of that information determines its classification according to confidentiality, privacy, and sensitivity, and determines who has the right to access and view it, or whether the information requires an encryption process before it is made available or completely blocked, based on that, it is applied to the data through specialized programs, and from here those programs must be compatible with those requirements throughout all stages of data transmission, and there is a globally recognized evaluation. programs that cover those gaps in information security and protection.

Request a Consultation or Training
Please feel free to contact us for any inquiry




















